Expert Explains Cancer May Be Metabolic Disease, and Shares a Cure
“Cancer is not a genetic disease, it’s a metabolic disease,” Thomas N. Seyfried, a well-known scholar in cancer research and a Professor of Biology at Boston College, told The Epoch Times. “Once people understand that cancer is a metabolic disease, then you will begin to see a very big reduction in death and greatly improved quality of life and survival.”
Cancer Has Remained High for Decades
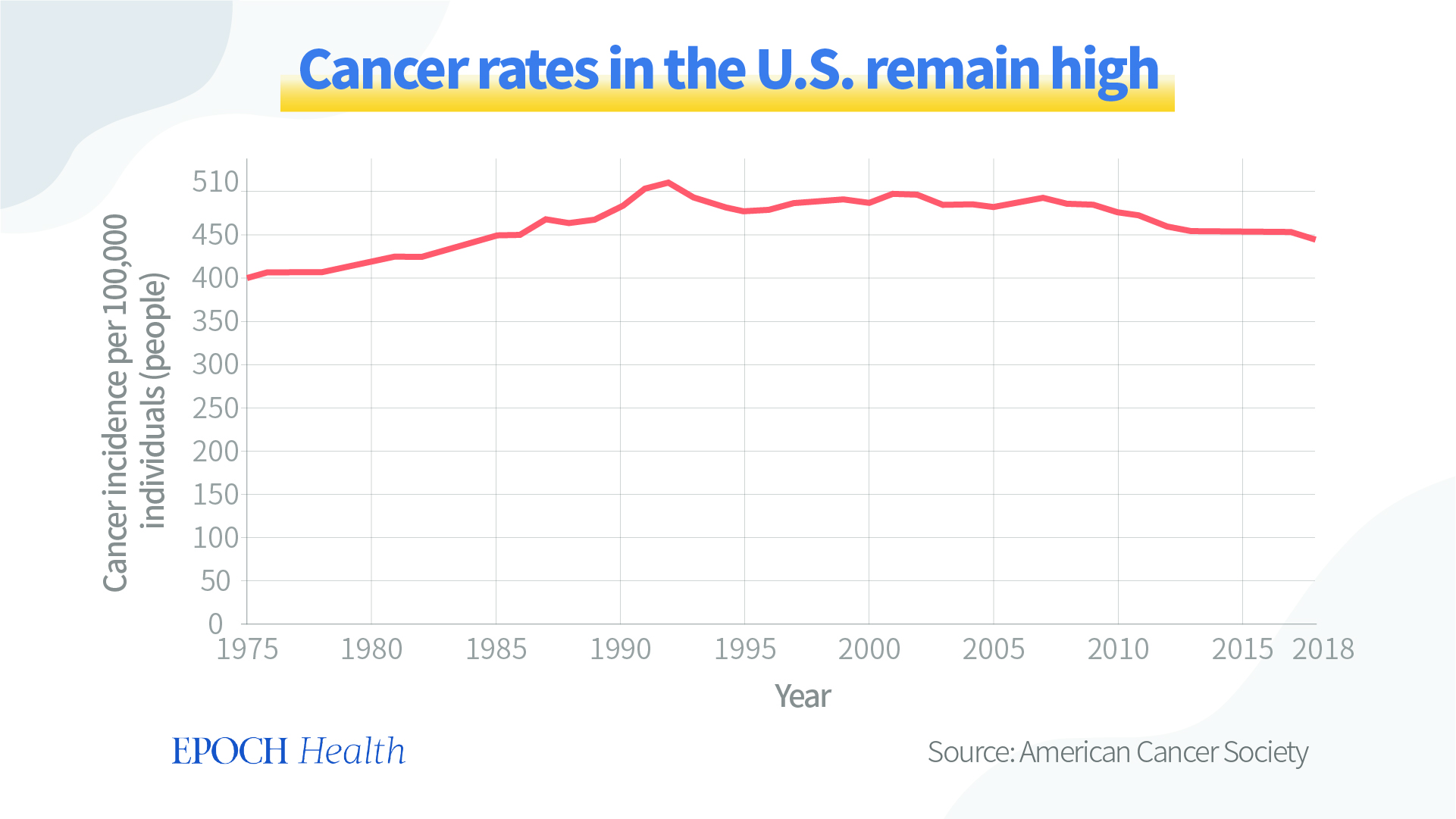
According to the statistics of the American Cancer Society, although the incidence of cancer in the United States has been declining slowly since the beginning of the 21st century, if we look at it over an extended period of time, we will find that the incidence of cancer is actually increasing, not decreasing.
In 1975, approximately 400 out of every 100,000 Americans had cancer. By 2018, that number had grown to roughly 445, an increase of more than 10 percent [1].
From the perspective of cancer mortality, in the past nearly 100 years, the number of women who died of cancer per 100,000 Americans has gradually declined from roughly 190 in 1930 to 130 in 2022; whereas cancer deaths among men per 100,000 Americans rose from around 160 in 1930 to 180 in 2022 [2].
In 2022, nearly 2,000,000 new cancer cases are expected in the United States, and over 500,000 people are expected to die from it. This means that every day, on average, 5,000 Americans are diagnosed with cancer, and over 1,600 people die from it [3].
Cancer May Not Be a Genetic Disease
“Why are so many people dying from cancer?” Seyfried asked. “Because the theory is wrong. The theory that underlies cancer is incorrect.”
Cancer is still generally considered a genetic disorder. Medical textbooks use somatic mutation theory to explain the cause of cancer. These textbooks state that cancer is caused by mutations in proto-oncogenes or tumor suppressor genes [4], and the mutated cells then multiply indefinitely and form malignant tumors. However, Seyfried mentioned a number of facts in this interview and in his published research [5] that are inconsistent with the above theory:
- Some cancers do not have genetic and chromosomal mutations;
- Some carcinogens do not cause gene mutation;
- Carcinogenesis also occurs in normal cells, but some do not develop further into cancerous cells;
- The result of studying cancer as a genetic disorder is the development of personalized treatment or precision medicine, but there are off-target effects for some customized cancer precision medicines.
- Ancient people from thousands of years ago rarely had cancer, nor did the indigenous people living in the natural environment.
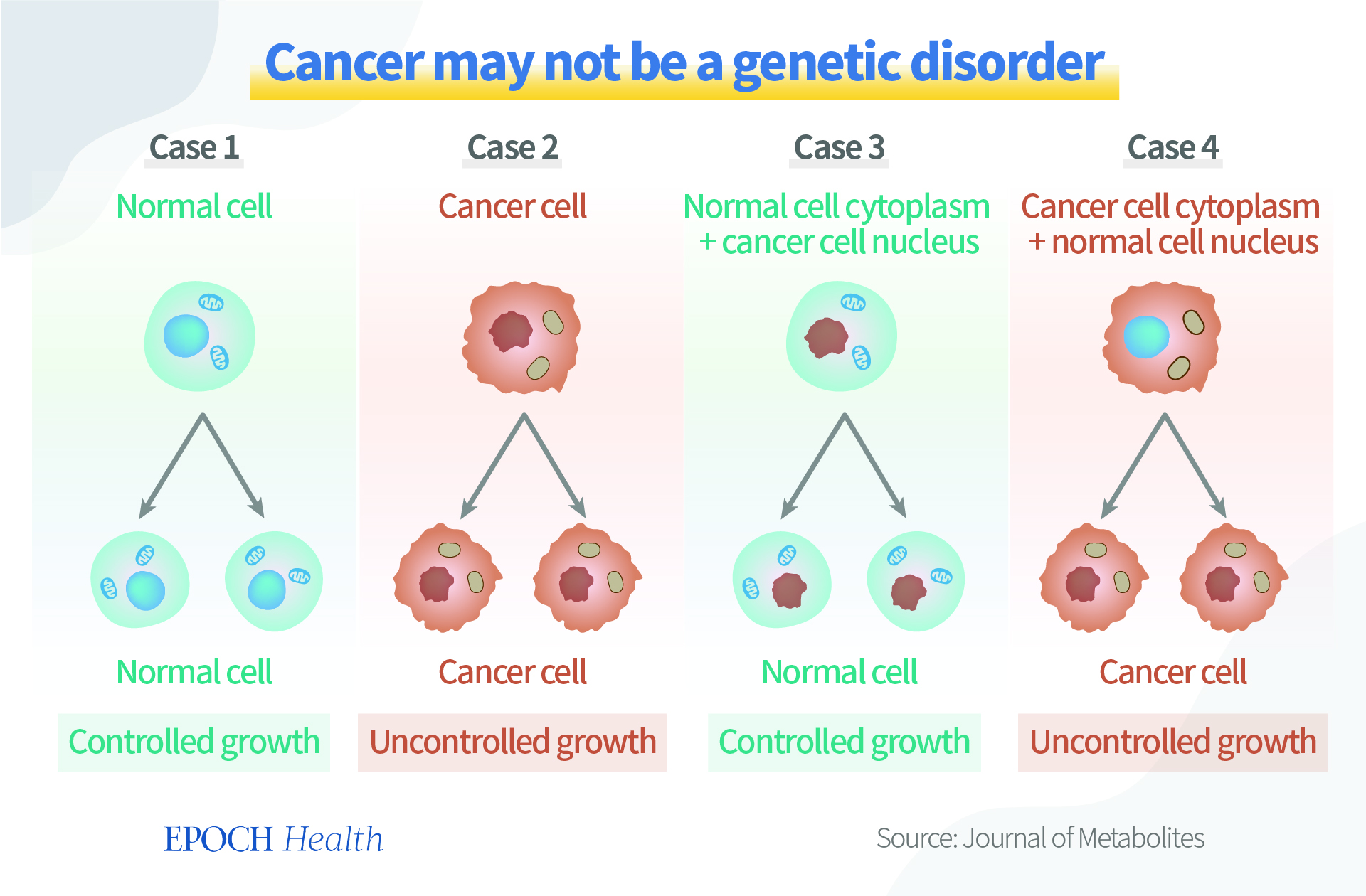
Seyfried also conducted experiments on nuclear and cytoplasmic transplantation [6], providing evidence for the possibility that cancer is not a genetic disorder.
Under regular circumstances, normal cells develop into normal cells with controlled growth (case 1 in the figure below), while cancer cells develop into cancerous cells with uncontrolled growth (case 2).
Genes are stored in the nucleus. When the nucleus of a cancer cell was implanted into a cytoplasm containing normal mitochondria, the cell developed into a normal cell anyway (case 3). According to the somatic mutation theory, a cell with a cancer cell nucleus should have developed into a cancer cell.
However, when the researchers implanted a normal nucleus into a cancerous cytoplasm with abnormal mitochondria, they found that it still developed into a cancer cell (case 4).
The Biggest Difference Between Normal Cells and Cancer Cells
The theory that cancer is a metabolic disorder was first proposed about 100 years ago by a well-known German scientist named Otto Warburg. Normal cells break down glucose through aerobic respiration, but Warburg observed that cancer cells are different. Cancer cells obtain energy through fermentation, even in an aerobic environment. Thus, Warburg proposed, aerobic respiratory insufficiency is the origin of cancer.
Seyfried’s research adds another metabolic pathway in cancer cells that Warburg did not observe: cancer cells also get a lot of energy from the fermentation of an amino acid called glutamine, which updated Warburg’s theory [7][8].
The truth, Seyfried said, is that “They [cancer] cannot breathe … they can’t get energy through oxygen, they can only get energy from fermentation.” All cancers can survive without oxygen, but they “cannot live without sugar, glucose, and the amino acid glutamine.”
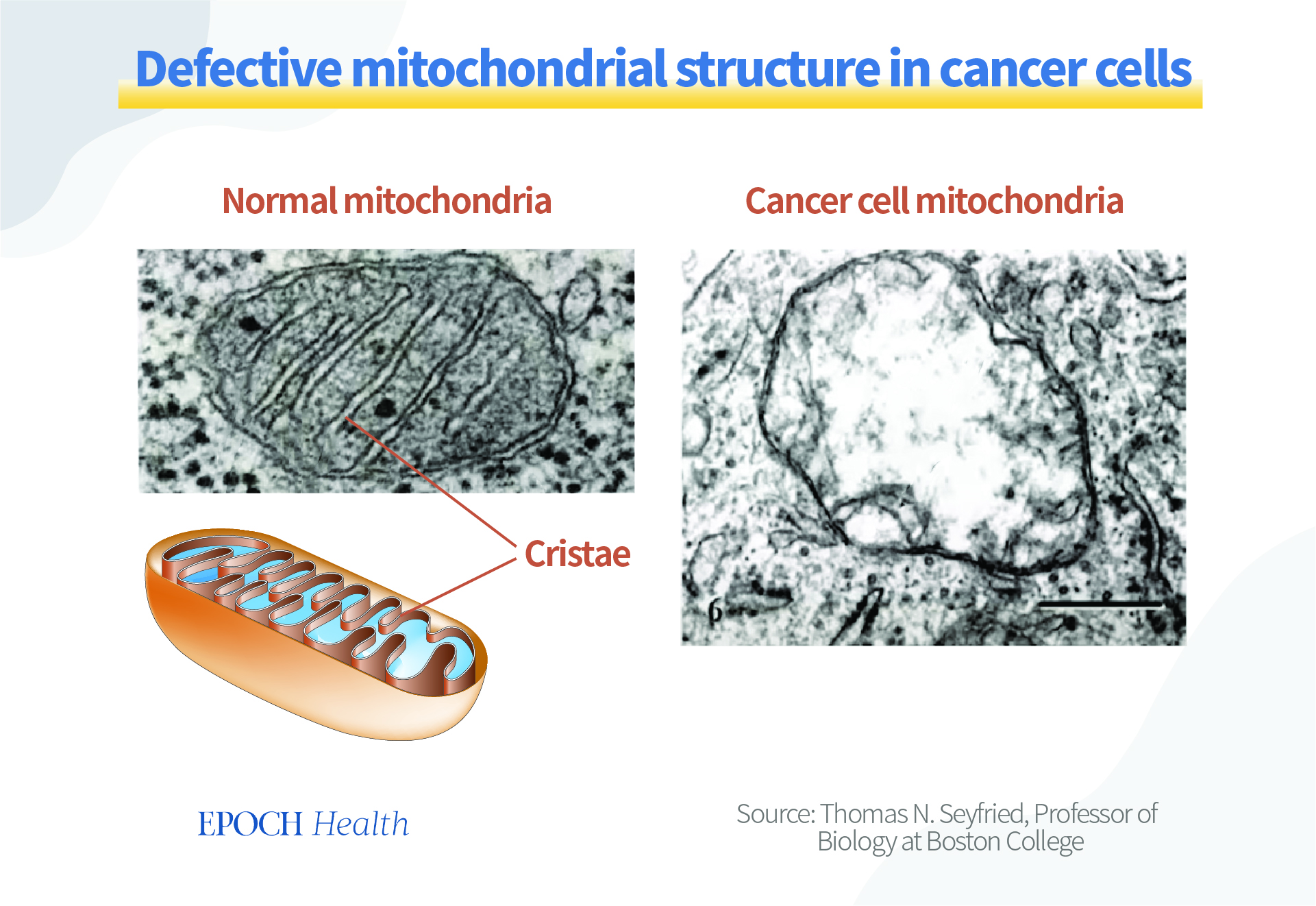
Cellular aerobic respiration mainly takes place in mitochondria. Mitochondria, which are responsible for respiration, are damaged and hollow in all major types of cancer. The cristae, the wrinkled and wavy structures in the mitochondrial structure, are cluttered and defective. The abnormality of mitochondrial structure will change the function of mitochondria, resulting in the inability of cells to obtain energy through oxidative metabolism. This changes the cell’s metabolism from relying primarily on oxidation to fermentation.
Seyfried further explained that the various abnormalities in cancer cells are caused by the loss of normal function of cell mitochondria due to various reasons (including carcinogens, radiation, pollution, inflammation, age, viruses, etc). A large number of reactive oxygen species (ROS) will be produced when mitochondria are damaged, further attacking and destroying the nucleus.
“The mutations that we see in cancer come as the result of damage from reactive oxygen species,” Seyfried said. “The mutations are an effect, they are not the cause of cancer.”
Why do all cancers have the same metastatic process? How does this relate to the theory that cancer is a metabolic disorder?
Seyfried said that the mitochondrial metabolic theory explains cancer metastasis better than the somatic mutation theory. After macrophages engulf and fuse with the defective proto-cancer cells, the normally functioning mitochondria are gradually replaced by dysfunctional mitochondria due to inflammation. As immune cells, macrophages have the ability to travel around the body. As a result, these cancer cells, which are fusions of proto-cancer cells and macrophages, spread throughout the body.
Stress Pulse Therapy: Adjust Cancer Cell Metabolism to Improve Condition
Seyfried believes the existing cancer treatment system is “broken.” He said once people understand the metabolic theory of cancer, treatments like chemotherapy and radiotherapy will be replaced by new treatments.
Based on the theory, Seyfried and his team developed the “stress pulse therapy” [9][10][11], which is a cocktail treatment consisting of the ketogenic diet, glutaminase inhibitor medicine, and stress management.
The ketogenic diet is adopted because cancer cells have defective mitochondria and impaired metabolism, so they can only rely on fermented sugars and glutamine for energy. Cancer cells cannot obtain energy as ketone bodies cannot be fermented. As for cells with normal metabolic function, they can obtain energy by metabolizing ketone bodies [12].
The purpose of a ketogenic diet combined with basic drugs is to control the ratio of glucose and ketone bodies in the blood to an ideal range while inhibiting the ability of cancer cells to acquire glutamine. In this way, we can “starve” cancer cells from a metabolic perspective, thereby achieving the same effect as cancer treatments.
An important aspect of “stress pulse therapy” is stress control and emotional management. Seyfried emphasized in the interview that people’s mental stress has a direct relationship with the development of cancer. When patients are diagnosed with cancer, they experience extreme panic and cannot rest or eat in peace. Excessive stress can raise blood sugar levels, which can feed cancer cells into rapid growth. As a result, cancer cannot be controlled. Easing the emotional and stress levels of the patient and his or her family can further stabilize the patient’s psychological and physical condition.
There have been many successful cases of cancer control by managing metabolism. Moreover, many patients use this method when traditional cancer treatments, such as chemotherapy and radiotherapy, are ineffective, or when cancer has spread.
A 38-year-old man developed symptoms in February 2016 and was subsequently diagnosed with glioblastoma multiforme (the most common and malignant form of primary adult brain cancer). After 20 months of ketogenic diet therapy and completion of chemotherapy and radiotherapy, the patient’s tumor decreased by approximately 1.5 cm in diameter. He seemed in good health with no apparent clinical or neurological deficits [13].
Another 54-year-old man was diagnosed with lung cancer; the cancer cells had metastasized and tumors were found in his brain. Radiotherapy and chemotherapy had no effect, so the patient opted for a ketogenic diet. Two years later, the tumors in his brain and lungs shrank; after nine years of treatment, the brain and lung cancer tumors remained stable in size [14].
A 45-year-old woman in Ohio was diagnosed with breast cancer in late 2016. In August 2018, the cancer had spread and she developed tumors in her brain, lungs, mediastinum, liver, abdomen, and bones. Her doctor expected her to have less than a month to live. The patient began receiving stress pulse therapy in November 2018. In April 2019, the scan report indicated that the treatment was effective. According to the published study, her last check-up was in March 2021 and the results showed a stable condition, no recurrence, and improved quality of life [15].
In a study published in the Clinical Nutrition journal, 80 patients with locally advanced and metastatic breast cancer were randomly assigned to a ketogenic diet or a control group for a 12-week treatment test. Patients in the ketogenic diet group had lower serum insulin levels, and their tumors shrank [16].
Two papers recently published in Nature: Prostate Cancer and Prostatic Disease describe the therapeutic benefits of a low-carb diet and a fasting-mimicking diet for patients with prostate cancer [17][18]. A ketogenic diet, which requires fasting and has low carbohydrates, can lower blood sugar levels and control tumor growth. These findings support the hypothesis that elevated ketone bodies are associated with reduced tumor growth [19].
Exercising, Fasting, and Avoiding High-Carb Diets May Keep Cancer Away
As for how an average person can maintain a healthy metabolism and prevent cancer, Seyfried said that by keeping the mitochondria in cells healthy, people are less likely to get cancer. He said this can be achieved through a certain period of fasting (drinking only water), a low-carb diet, and exercise.
He also emphasized that high carbs and unnutritious foods such as junk food can cause cancer, and advised to stay away from such foods. It’s not just cancer, diseases like Alzheimer’s, Type 2 diabetes, and obesity, among others are all related to the Western diet.
“As soon as the Western diet comes into the population, you get cancer … and diabetes and things like this.” He also joked, “The bottom line is don’t eat anything and you’ll get very healthy. Just drink water.”
Republished from: https://www.theepochtimes.com/health/expert-explains-cancer-may-be-metabolic-disease-and-shares-a-cure_4840835.html
How Linoleic Acid Wrecks Your Health".

.png)
.png)




.png)

.png)
Comments
Post a Comment